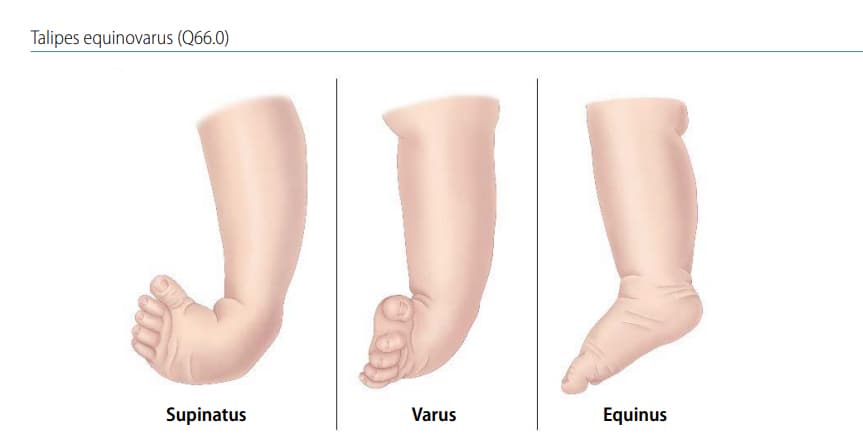
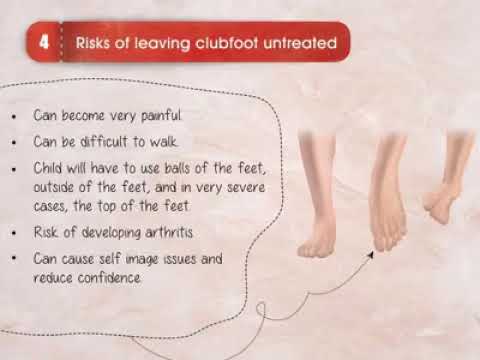
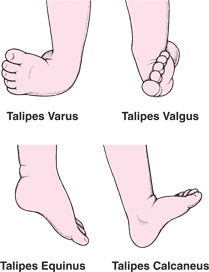
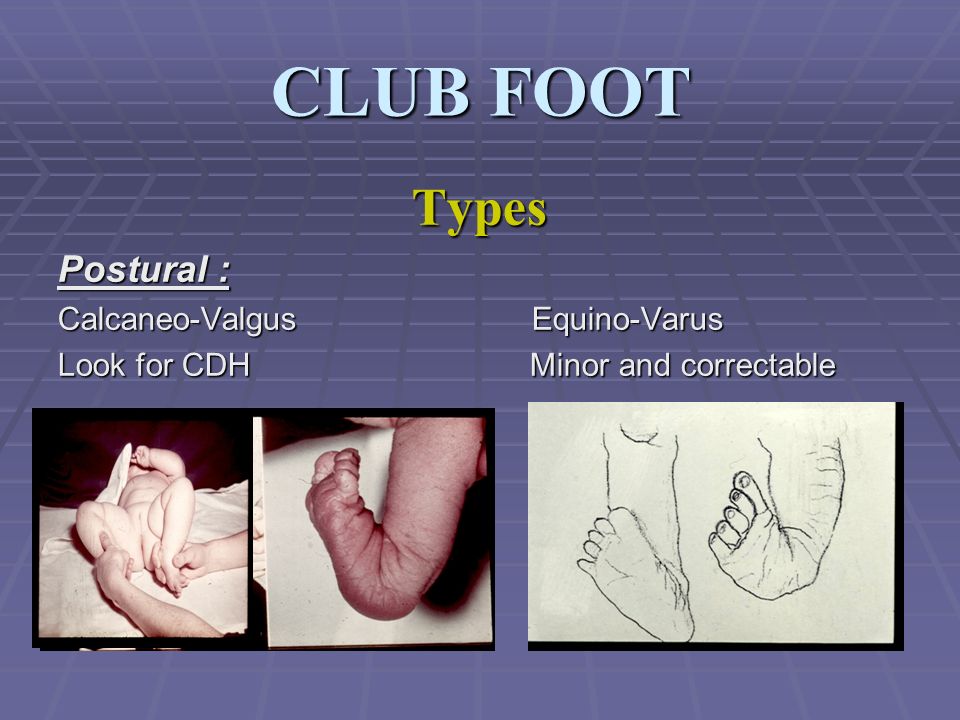
Major structural anomalies are the conditions that account for most of the deaths, morbidity and disability related to congenital anomalies (see Box 11 for a list of selected external and internal major congenital anomalies) In contrast, minor congenital anomalies, although more prevalent among the population, are structural changes that pose There are several types of Clubfoot calcaneal valgus – the foot is angled at the heel with the toes pointing upward and outward matatarusus varus – the front of the foot is turned inward talipes equinovarus – the foot is turned inward and downward Clubfoot can also be divided into two categories an isolated type and a type associated with other congenital birth defectsCongenital Deformity and Clubfoot Congenital deformities of the lower limbs are developmental disorders that are present at birth, causing alterations in the shape and appearance of the legs Several factors such as genetics, teratogenic drugs, and chemicals can cause congenital

Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram
Are there different types of clubfoot
Are there different types of clubfoot-Treatment of Congenital Club Foot Treatment of Congenital Club Foot J Bone Joint Surg Am 1992 Mar;74(3) Author I V Ponseti 1 Publication types Review MeSH terms Clubfoot / therapy* Equinus Deformity / congenital* Equinus Deformity / therapy*Congenital talipes equinovarus, or club foot, is one of the commonest congenital orthopaedic conditions Its incidence in the UK is approximately live births and up to 50% of cases are



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine
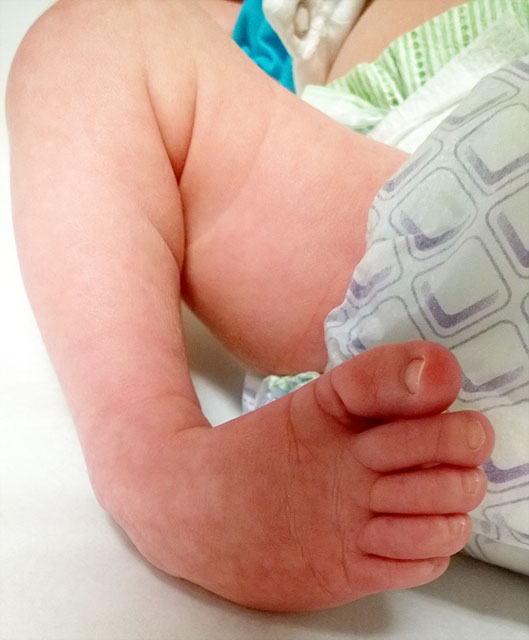
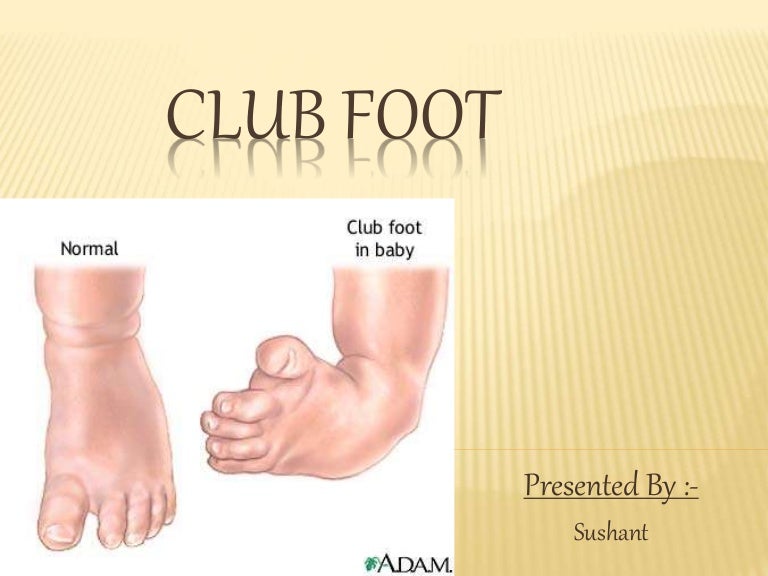
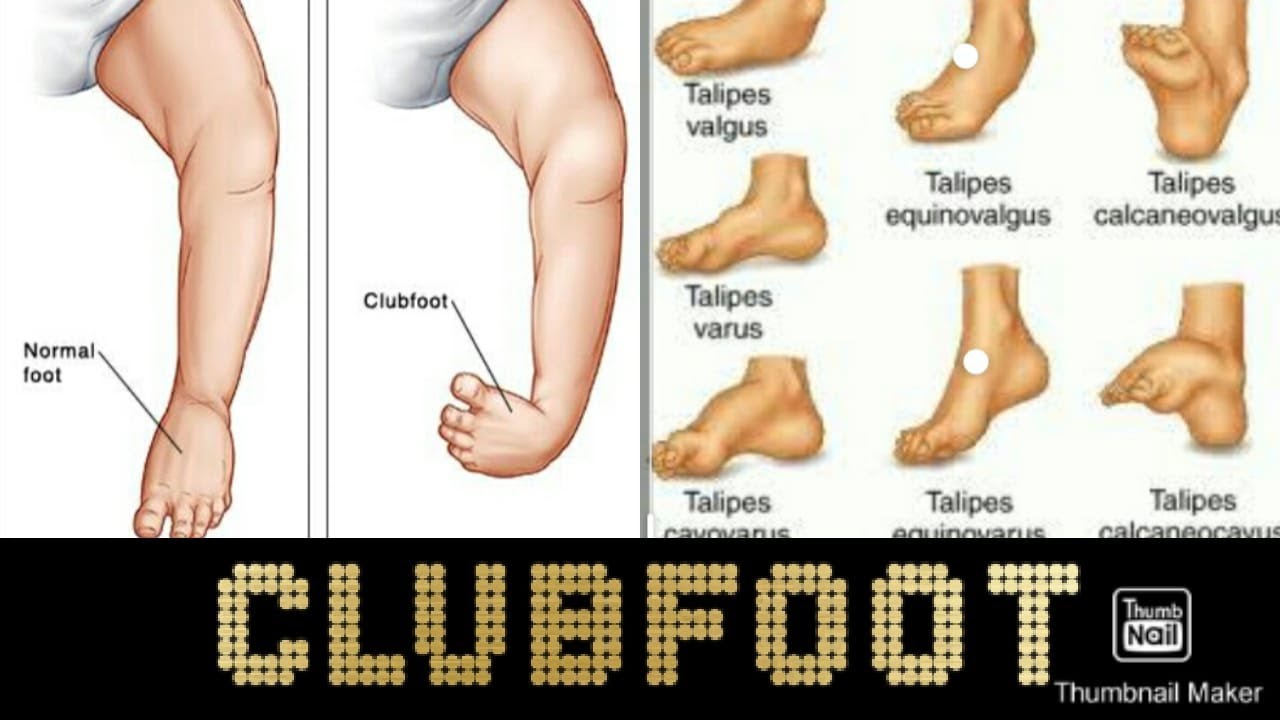
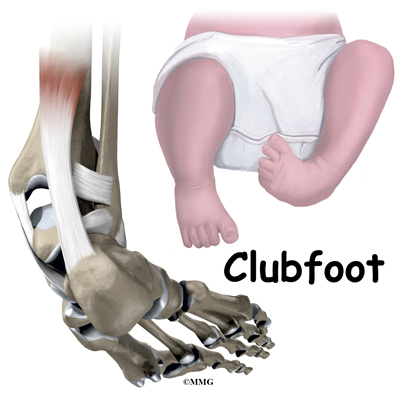
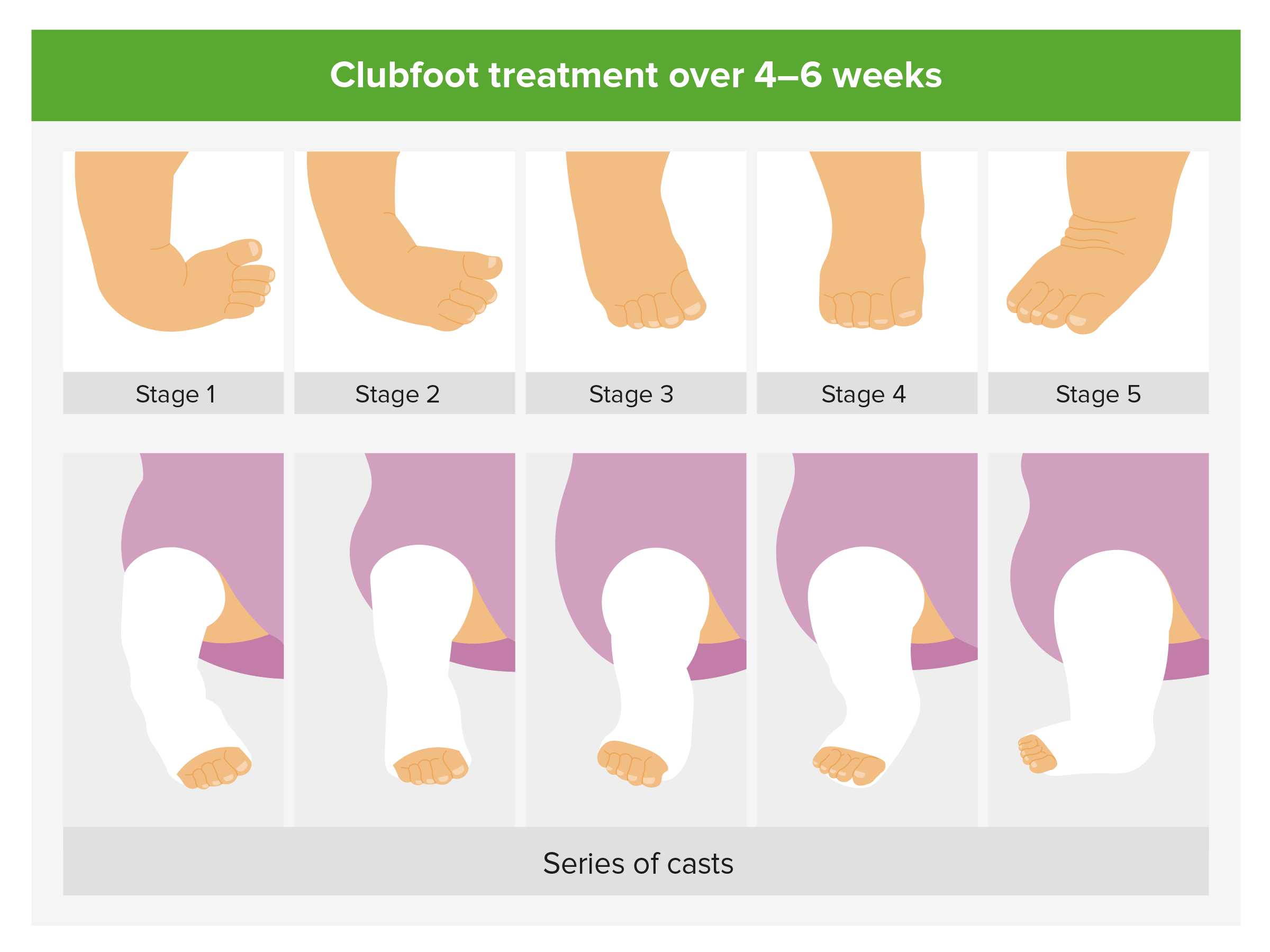
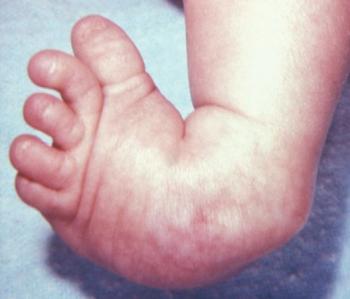
Pediatric Clubbed Foot Clubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus, is a congenital (present at birth) foot deformity It affects the bones, muscles, tendons and blood vessels and can affect one or both feet The foot is usually short and broad in appearance and the heel points downward while the front half of the foot (forefoot) turns inwardKeywords Ponseti treatment, Congenital club foot, Abduction bracing, Tibialis tendon transfer, Club foot casting, Foot abduction brace, Manipulation Introduction Treatment of congenital club foot has changed radically with the introduction of the Ponseti method in most paediatric orthopaedic centres worldwide during the last ten to 15 years Congenital Anomalies and Deformations of the Musculoskeletal System Talipes Equinovarus Related Pages Talipes equinovarus (TEV) is the specific term and common type of what is sometimes called "clubfoot", a term that encompasses a range of anomalies of the ankle or foot present at birth Be sure to differentiate TEV from other types
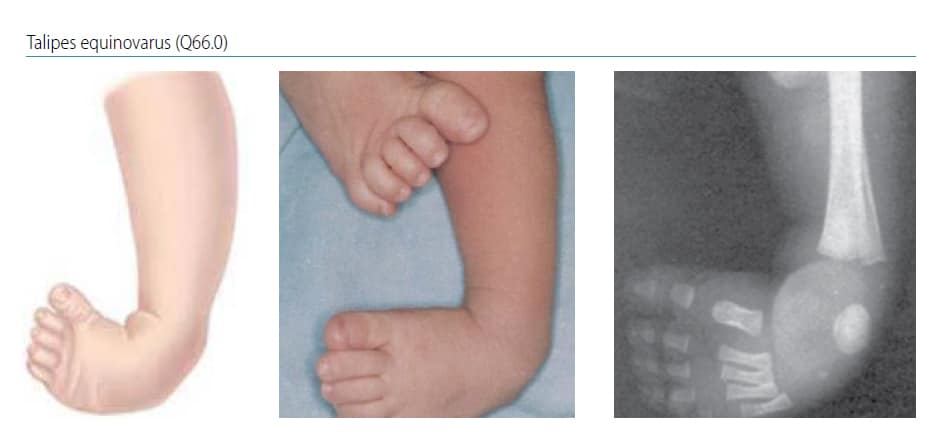
CONGENITAL TALIPES EQUINO VARUS (CLUB FOOT) INTRODUCTION Congenital talipes equinovarus, also known as 'club foot', is a congenital foot deformity present at birth It is one of the most common congenital deformities The foot consists of 26 bones Most relevant for this congenital deformity are the talus, calcaneus and navicularThere are two types of clubfoot Isolated or idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type If your child has clubfoot with no other medical problems, it's called isolated clubfoot Idiopathic means that the cause of clubfoot is not known Nonisolated congenital talipes equinovarus (club foot/ctev) ppt by dr pratik 1 congenital talipes equinovarus dr pratik agarwal dr madhav khadilkar 2 outline • what is ctev?
Idiopathic clubfoot The most common type of clubfoot is idiopathic, which means the cause is unknown Idiopathic clubfoot is not related to any other medical problems Feet of babies with this type of clubfoot are stiff and hard to manipulate Syndromic clubfoot Syndromic clubfoot occurs when the condition is part of a larger syndrome This type is usually more severe and difficult toClubfoot or talipes is a congenital deformity of the foot that occurs in approximately births with half of them being bilateral (both feet) and it is twice as common in boys as in girls The foot has a typical appearance of pointing downwards and twisted inwards Since the condition starts in the first trimester of pregnancy, theClubfoot, also known as Congenital Talipes Equinovarus, is a complex, congenital deformity of the foot, that left untreated can limit a person's mobility by making it difficult and painful to walk 1 It is defined as a deformity characterized by complex, malalignment of the foot involving soft and bony structures in the hindfoot, midfoot



Ponseti Method Physiopedia




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets
The most common type of club foot is congenital talipes equinovarus clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a developmental deformity of the foot one of the most common birth deformities with an incidence of 12 per 1000 live births each year in the white population (1,2) clubfoot is twice as common in boys and is bilateralTalipes Equinovarus / Clubfoot Discussion congenital clubfoot is a structural foot deformity that is present at birth; Abstract Congenital contractures are common in the newborn and can include single location contractures that include clubfeet, hip dislocations, and multiple congenital contractures (MCC) Talipes equinovarus, or clubfoot, is an abnormality of the foot position and can be isolated or part of a broader spectrum of anomalies



What A Paediatrician Should Know About Congenital Clubfoot Italian Journal Of Pediatrics Full Text




Current Concepts With The Ponseti Technique
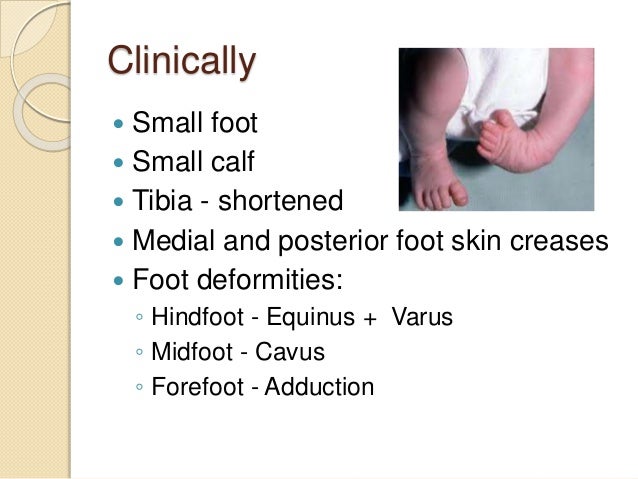
Articular malalignments are fixed by contracted joint capsules, ligaments, and contracted foot and ankle tendons; CLUB FOOT Types Idiopathic (Unknown Etiology) CongenitalTalipes EquinoVarus CTEV Acquired, Secondary to CNS Disease Spina bifida, Poliomyelitis Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Absent Bone fibula / tibia 10 CTEV MOST COMMON CONGENITAL FOOT DISORDER MALES 1/1000 LIVES BIRTHS 11There is in utero malalignment of the talocalcaneal, talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints;



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc



Congenital Clubfoot Youtube
Talipes equinovarus Incidence Clubfoot is a common defect present at birth and occurs in every 1,000 live births Bilateral TEV can be found be found in nearly 50% of cases About twice as many males are born with the congenital form than females Talipes equinovarus Types{{configCtrl2infometaDescription}} This site uses cookies By continuing to browse this site you are agreeing to our use of cookiesClub foot (also called talipes) is where a baby is born with a foot or feet that turn in and under Early treatment should correct it In club foot, 1 foot or both feet point down and inwards with the sole of the foot facing backwards Credit Club foot happens because the Achilles tendon (the large tendon at the back of the ankle) is too short




Current Concepts With The Ponseti Technique



What A Paediatrician Should Know About Congenital Clubfoot Italian Journal Of Pediatrics Full Text
Club Foot also is known as Giles Smith Syndrome, Congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV), or talipes equinovarus (TEV) The Word "Talipes Equinovarus" comes from Latin Talus (ankle) pes (foot)Equino– indicates the heel is elevated (like a horse's) varusindicates it is turned inward The foot is turned in sharply, and the person seems to be walking on their ankle Ontology Congenital clubfoot The most common congenital deformation of the foot, occurring in 1 of 1,000 live births The most common form is talipes equinovarus, where the deformed foot is turned downward and inward sharply A deformed foot in which the foot is plantarflexed, inverted and adducted• epidemiology • etiology • pathological anatomy • clinical features • classification • radiographic evaluation • treatment • summary 3 what is ctev?



Club Foot




Clubfoot Also Known As Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Is A Complex Congenital Deformity Of The Foot That Left Untreated Can Limit A Person S Mobility By Making It Difficult And Painful To Walk 1
Clubfoot is often broadly classified into two major groups Isolated (idiopathic) clubfoot is the most common form of the deformity and occurs in children who have no other medical problems Nonisolated clubfoot occurs in combination with various health conditions or neuromuscular disorders, such as arthrogryposis and spina bifida Clubfoot (congenital talipes equinovarus) Clubfoot, also known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is a common idiopathic deformity of the foot that presents in neonates Diagnosis is made clinically with a resting equinovarus deformity of the foot Treatment is usually ponseti method castingMost commonly, it is classified as "Idiopathic Clubfoot" which means there is no known cause "Secondary Clubfoot" which occurs when there is another disease or condition that is causing or is linked to the clubfoot, such conditions are usually neurological or syndromic disorders such as Arthrogyposis or Spina Bifida




Clinical Photographs Showing A The Club Feet Of A 1 5 Month Old Baby Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health
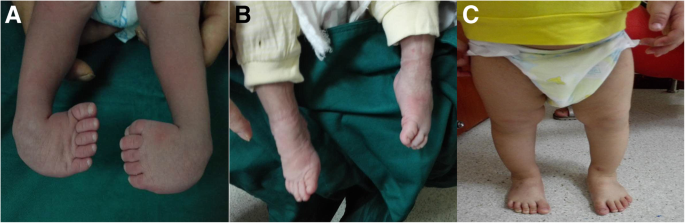
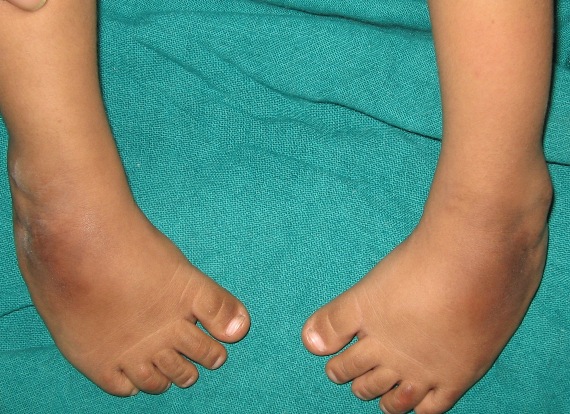
Most types of clubfoot are present at birth (congenital clubfoot) Clubfoot can occur in one foot or both feet In almost half of affected infants, both feet are involved Although clubfoot is painless in babies, treatment should begin immediately, as delaying therapy can cause significant problems as the child growsIn some cases, clubfoot can be associated with other abnormalities of the skeleton that are present at birth (congenital), such as spina bifida, a serious birth defect that occurs when the tissue surrounding the developing spinal cord of a fetus doesn't close properlyClubfoot is a foot deformity classified into three different types idiopathic (unknown cause), neurogenic (caused by condition of the nervous system) and syndromic (related to an underlying syndrome) Idiopathic Clubfoot Also known as talipes equinovarus, idiopathic clubfoot is the most common type of clubfoot and is present at birth




Club Foot




Clubfoot Flip Ebook Pages 1 Anyflip Anyflip
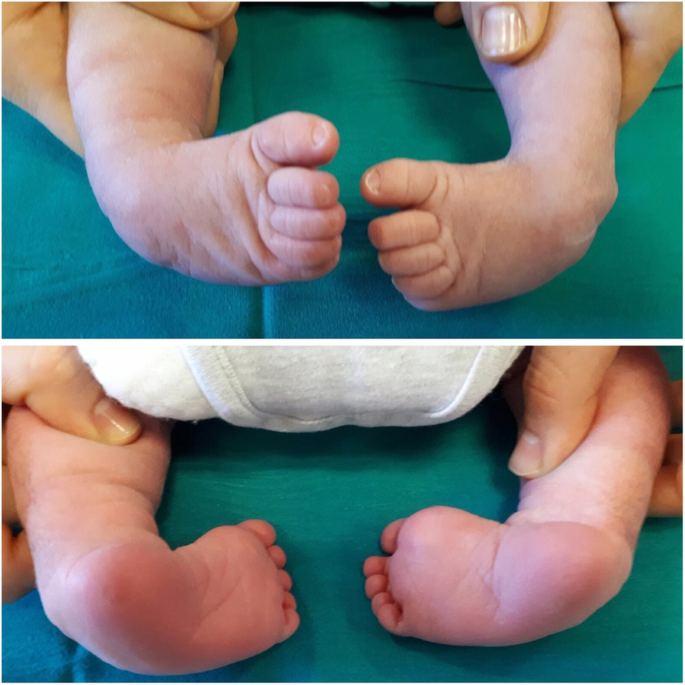
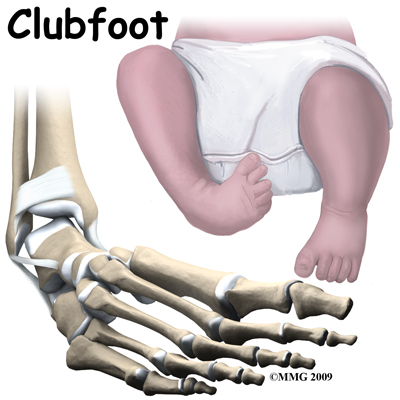
Clubfoot is the most frequent congenital malformation of the foot, affecting more than 1–2 subjects per 1000 newborns Without appropriate treatment, a child with congenital clubfoot will never be able to walk physiologically with a dramatic impact on the quality of life In the last decades, different corrective solutions have been proposed, and there is rising scientific Introduction Congenital clubfoot is one of the most common limb disorders in humans with a prevalence of 1–2/1000 live births among Caucasians 1 The deformity appears with an adductus of the forefoot, a cavus of the midfoot, and an equinovarus of the hindfoot, for which there is a wide variation in clinical severity 2 There are many theories concerning theClubfoot, also known as talipes equinovarus (TEV), is a common foot abnormality, in which the foot points downward and inward It occurs twice as often in males than in females Signs of clubfoot include a short and/or tight Achilles tendon (heel cord) and a heel that is turned in



Physical Therapy In Plymouth For Pediatric Issues Clubfoot



1
Clubfoot, known as congenital talipes equinovarus, is one of the complex paediatric foot deformity with the incidence of 1 in every 1000 live births It consists of four complex foot abnormalities such as forefoot adductus, midfoot cavus, and hindfoot varus and ankle equinus Types Of Clubfoot A congenital defect, clubfoot can be of three types 1 Idiopathic Clubfoot Idiopathic or isolated clubfoot is the most common form of clubfoot deformity that is prevalent at the time of birth of a child This type of clubfoot affects one to four babies out of 1,000 live births This deformity is characterised by a stiff and Club Foot Talipes equinovarus (once called club foot) is a deformity of the foot and ankle that a baby can be born with It is not clear exactly what causes talipes In most cases, it is diagnosed by the typical appearance of a baby's foot after they are born The Ponseti method is now a widely used treatment for talipes



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



Congenital Clubfoot Early Recognition And Conservative Management For Preventing Late Disabilities Springerlink
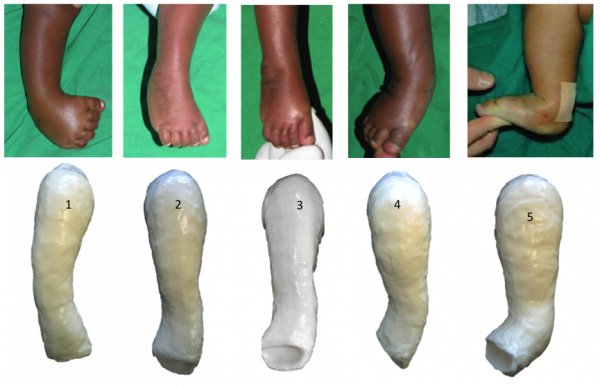
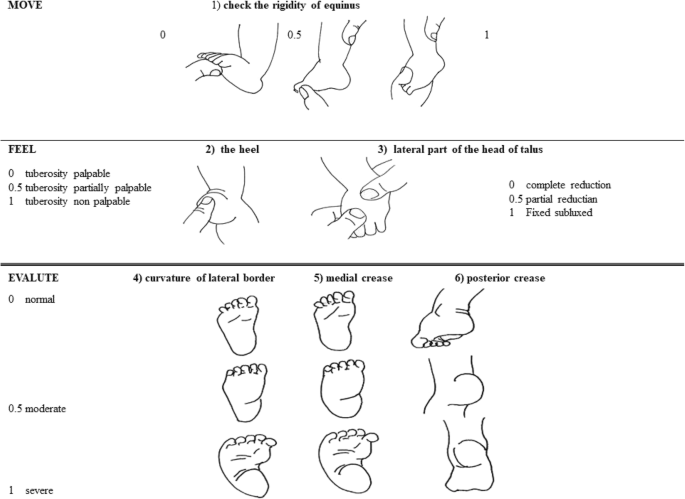
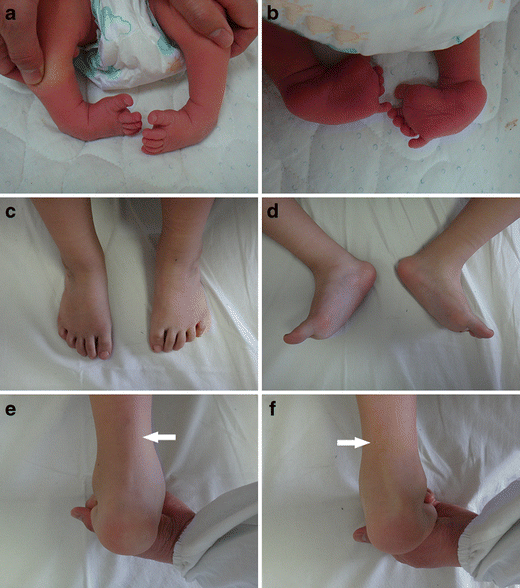
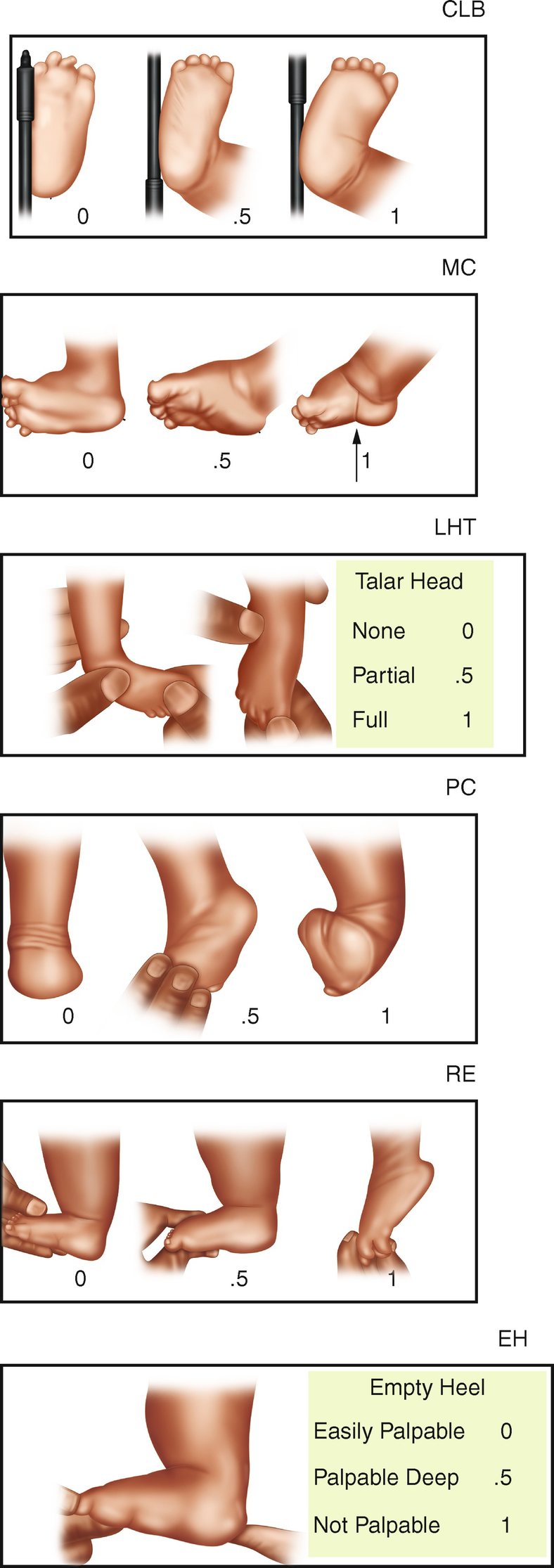
Extrinsic (supple) clubfoot deformity What is the deformity in which one foot has congenital talipes equinovarus and the other has congenital convex pes plano valgus?Clubfoot (talipes equinovarus) is a birth defect in which the foot and ankle are twisted out of shape or position The usual clubfoot is a down and inward turning of the hind foot and ankle, with twisting inward of the forefoot Sometimes the foot only appears abnormal because it was held in an unusual position in the uterus (positional clubfoot)Congenital clubfoot is differentiated by structural, postural and secondary type The postural clubfoot can occur by abnormal position during birth and manipulative control The patient should be thoroughly examined to assess the features of paralytic clubfoot Congenital clubfoot can be rectifying completely Diagnostic tests Table 1 Pirani scoring



Congenital Talipus Equino Varus Physiotherapy Treatment In Ahmedabad




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics
Although different types of clubfoot exist, the condition is usually accompanied by the following foot deformities Plantar flexion Twisting of the ankle Cavus foot deformity An unusually high arch in the foot Varus An inversion of the heel that causes the front ofWhich of the types of clubfoot deformities are more treatable with serial casting?Idiopathic clubfoot is an uncommon congenital deformity that clusters in families but does not fit typical Mendelian inheritance patterns Studies done on twins, different incidences in various ethnic groups, and transmission between generations all suggest



Clubfoot Its Types And Causes Simplified In Hindi Youtube




Clubfoot Pdf Pied Medecine Clinique



Chapter 4 9 Talipes Equinovarus Talipes Equinovarus Q66 0 Cdc




Prevalence And Characteristics Of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot In Northern Ghana A Two Year Retrospective Descriptive Study African Journal Of Current Medical Research
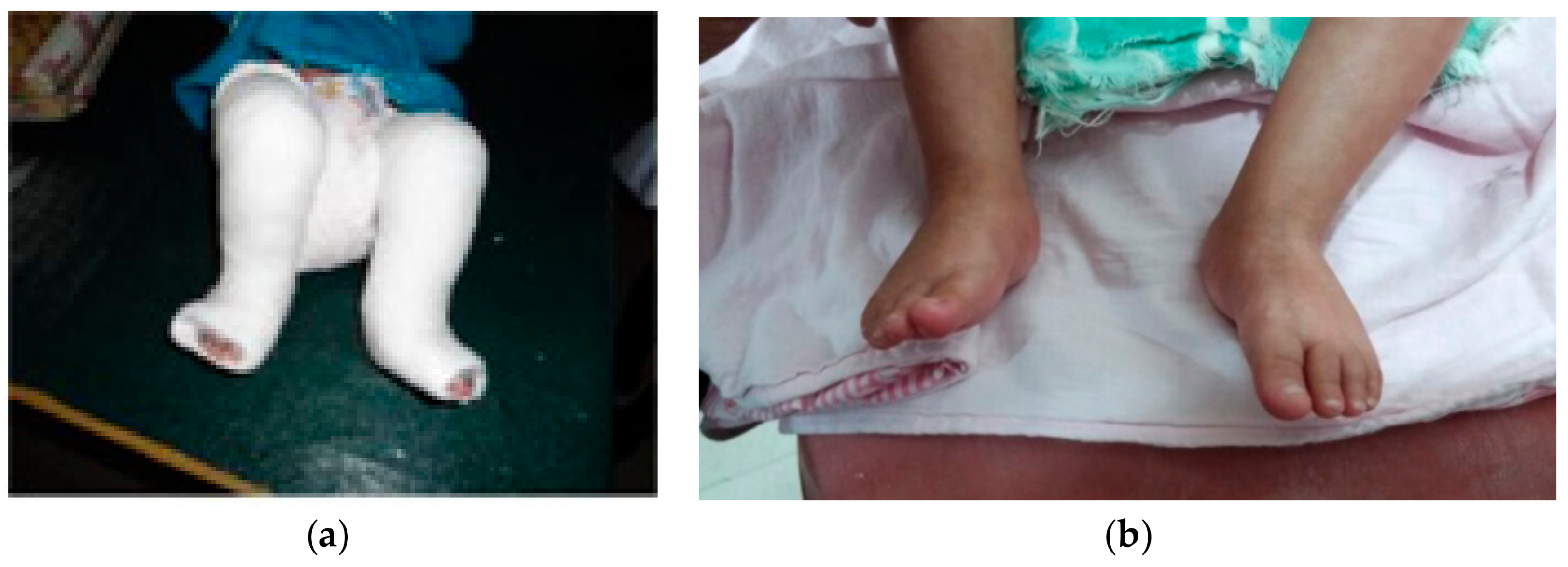



Children Free Full Text Ponseti Technique For The Management Of Congenital Talipes Equinovarus In A Rural Set Up In India Experience Of 356 Patients Html




Clubfoot And Its Treatment Dr Michael Vohrer




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine



2 Congenital Talipes Flip Ebook Pages 1 50 Anyflip Anyflip
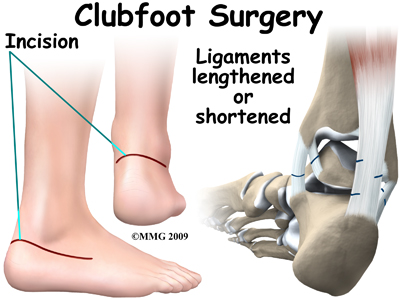



Physical Therapy In Long Island For Pediatric Issues Clubfoot
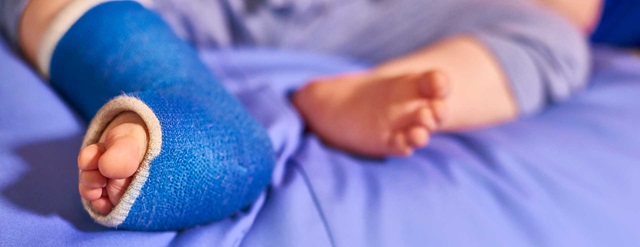



Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine
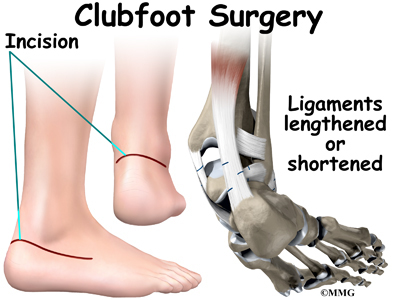



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com




Clubfoot Phenotype In Pma Pma Mice Human Newborn With Congenital Download Scientific Diagram




Clubfoot Wikipedia



2




Video Club Foot




Clubfooted Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Challenging Clubfeet The Arthrogrypotic Clubfoot And The Complex Clubfoot Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine



Clubfoot Eorthopod Com




Clubfoot Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis



Clubfoot Deformity Footeducation




98 Club Foot Illustrations Clip Art Istock



1




32 Clubfoot Ideas Club Foot Club Foot Baby Pediatric Physical Therapy
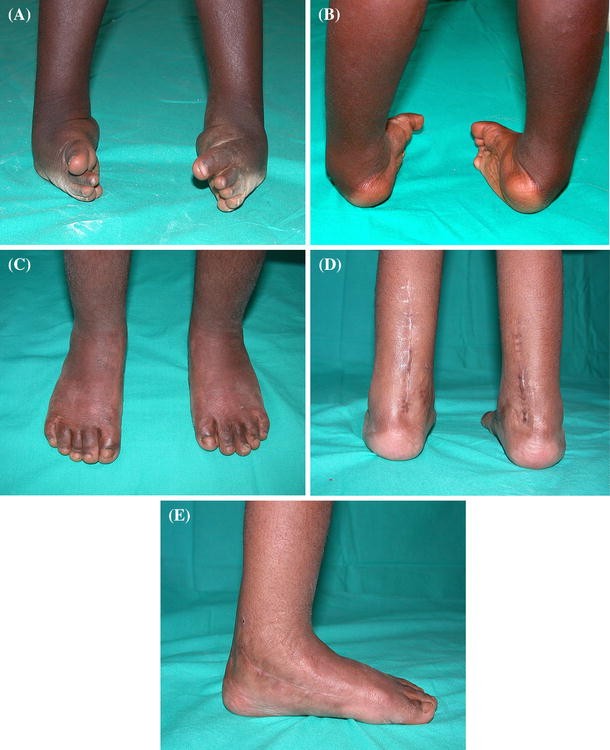



Congenital Idiopathic Talipes Equinovarus Before And After Walking Age Observations And Strategy Of Treatment From A Series Of Cases Journal Of Orthopaedics And Traumatology Full Text




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Final Ppt Powerpoint
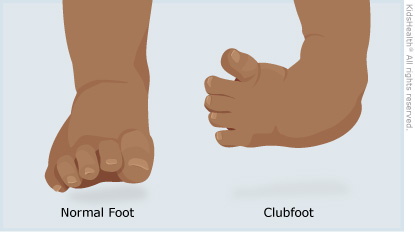



Clubfoot For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
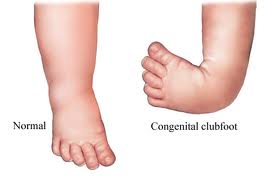



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
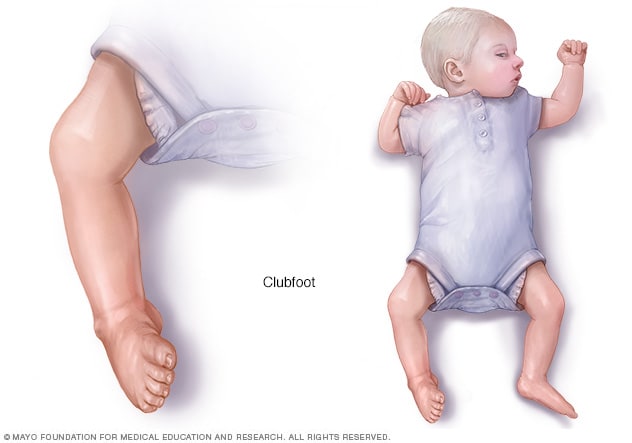



Clubfoot Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic



2



1




Club Foot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus About Club Foot Patient
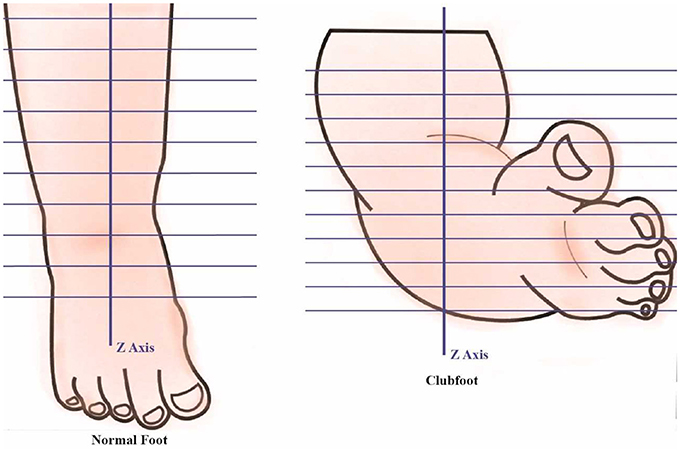



Frontiers Developing A Three Dimensional 3d Assessment Method For Clubfoot A Study Protocol Physiology




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Congenital Clubfoot Prof Mohamed M




Clubfoot Johns Hopkins Medicine



Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Congenital Clubfoot Ppt Video Online Download




Pdf Current Conservative Management And Classification Of Club Foot A Review Semantic Scholar




What Is Clubfoot Or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Ctev Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Physiotherapy Treatment Of Clubfoot Or Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Ctev




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Msd Manual Consumer Version




Pdf Congenital Idiopathic Talipes Equinovarus Before And After Walking Age Observations And Strategy Of Treatment From A Series Of Cases Semantic Scholar



Introduction To Clubfoot Physiopedia
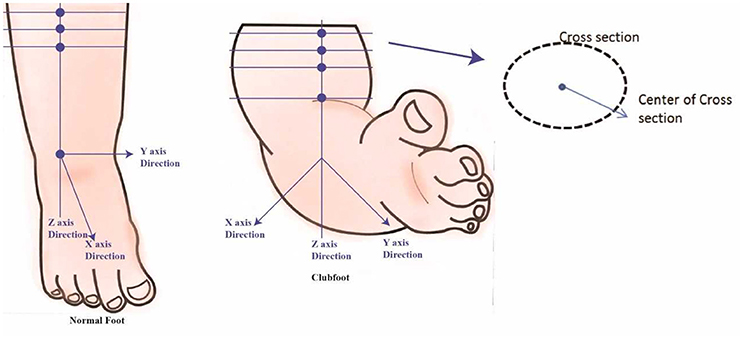



Frontiers Developing A Three Dimensional 3d Assessment Method For Clubfoot A Study Protocol Physiology



Foot Deformities Concise Medical Knowledge




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Narayana Health



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Orthopaedicprinciples Com



Clubfoot Causes And Treatments




Clubfoot



1



Clubfoot What Is Clubfoot What Causes Clubfoot Who Gets Clubfoot What Are The Symptoms Of Clubfoot




Congenital Club Foot In Child Kerala Nurses Hub Youtube



Clubfoot Orthoinfo os



A Polyaxial Fixation Brace For The Treatment Of Idiopathic Congenital Talipes Equinovarus In Newborns Journal Of Orthopaedic Surgery And Research Full Text



Congenital Clubfoot




Clubfoot And Other Foot Defects Children S Health Issues Msd Manual Consumer Version




Clubfoot Foot And Ankle Deformities Principles And Management Of Pediatric Foot And Ankle Deformities And Malformations 1 Ed



Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Or Club Foot Bone And Spine




Talipes Club Foot Doctors Australia



Clubfoot Symptoms Stages Definition Description Demographics Causes And Symptoms Diagnosis




What Is Clubfoot Symptoms And Treatment Familydoctor Org




Managing Children With Clubfoot Course Evaluation Report Physiopedia




Clubfoot Phenotype In Pma Pma Mice Human Newborn With Congenital Download Scientific Diagram
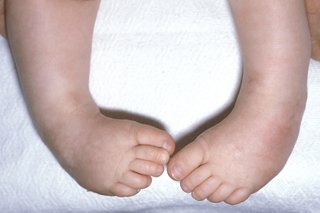



Club Foot Nhs



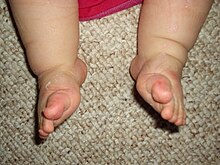
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Springerlink



Clubfoot Wikipedia




Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Pediatrics Orthobullets




Treatment Of Relapsed Residual And Neglected Clubfoot Adjunctive Surgery Journal Of Children S Orthopaedics




Congenital Clubfoot Genetic Disorders Types Of Clubfoot
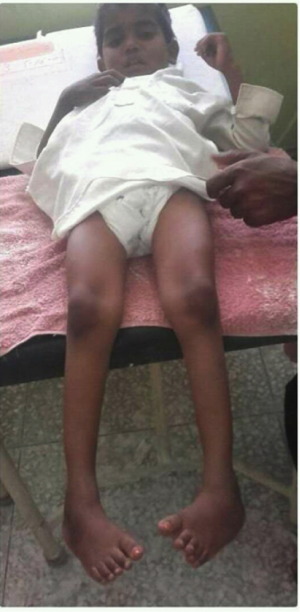



Neglected Bilateral Clubfoot Physiopedia




Clubfoot Wikipedia




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital




Club Foot Symptoms And Treatment



Club Foot Talipes Equinovarus Ankle Foot And Orthotic Centre
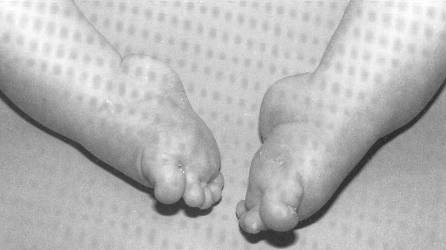



Clubfoot Congenital Equinovarus Cev Team Bone




Clubfoot Nurse Key




Club Foot




By Cassie Maier What Is Club Foot Club Foot Is When One Or Both Babies Feet Are Turned Inward And Downward And Cannot Be Put Into Normal Position Easily Ppt Download




Pdf Midterm Results Of The Ponseti Method In The Treatment Of Congenital Clubfoot Semantic Scholar
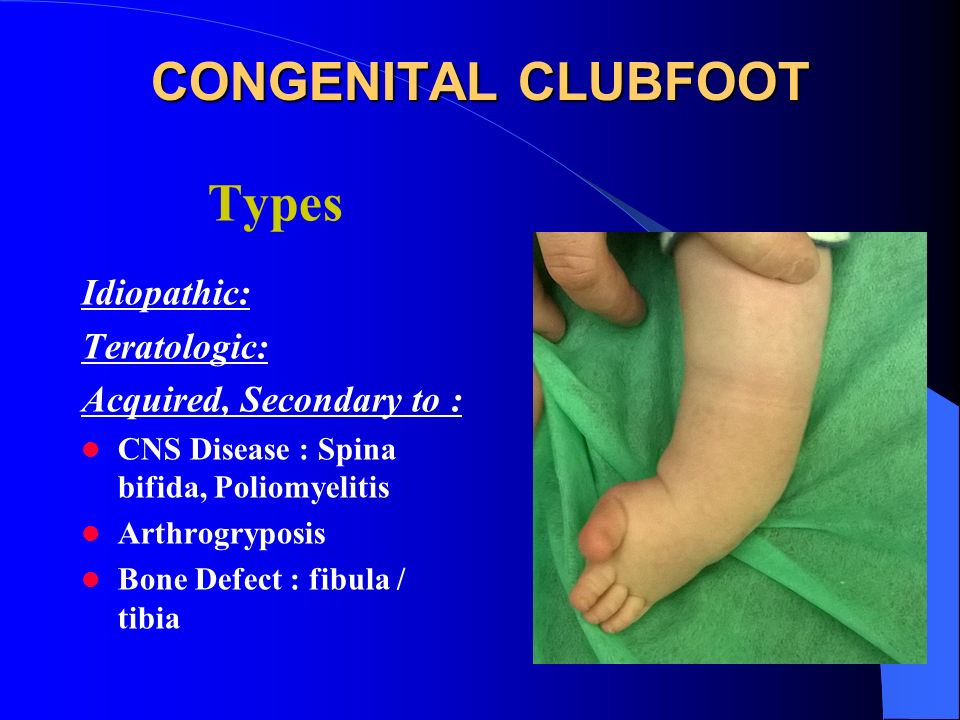



Congenital Clubfoot Congenital Talipes Equino Varus Ppt Video Online Download




Clubfoot Boston Children S Hospital




Club Foot Talipes In Babies Causes Signs Treatment Youtube
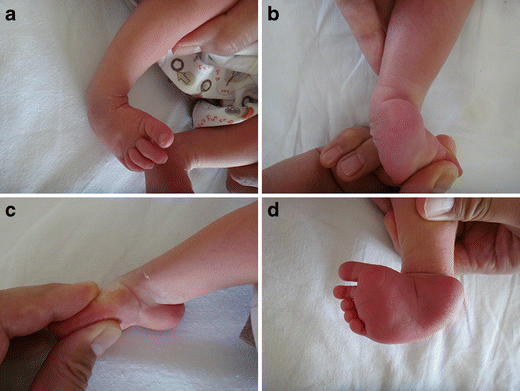



Congenital Clubfoot Early Recognition And Conservative Management For Preventing Late Disabilities Springerlink




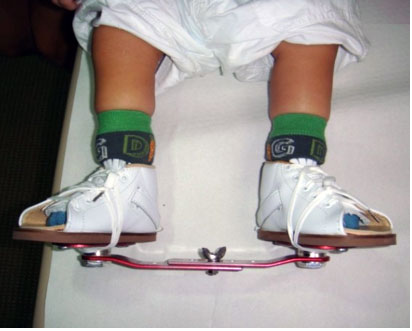
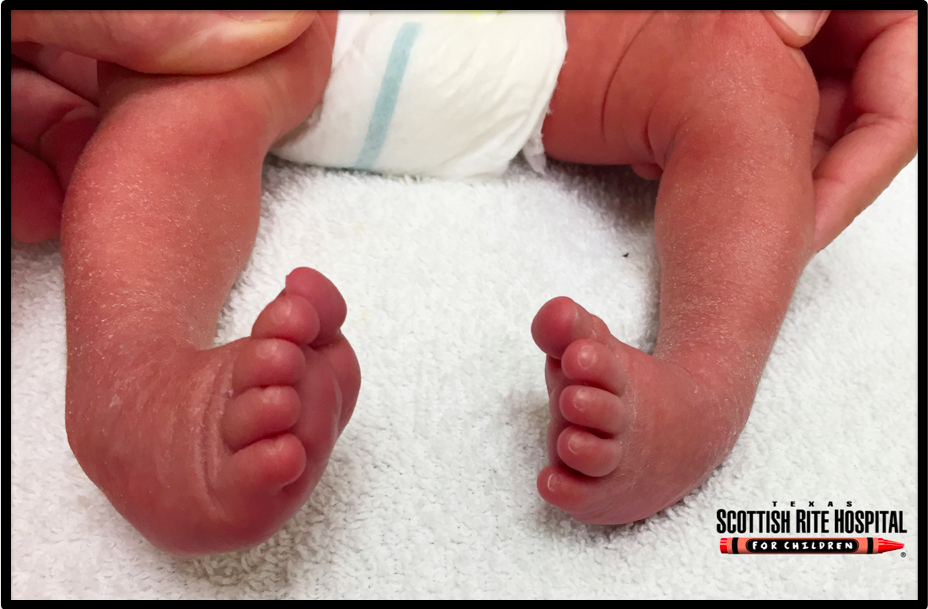
The Feet Of A Newborn With Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Deformity Download Scientific Diagram




Scielo Brasil Pe Torto Congenito Pe Torto Congenito




Congenital Talipes Equinovarus Clubfoot Nursing Care Management Pediatric Physical Therapy Medical Anatomy Physical Therapy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿